Troubleshoot: Windows + Local
Windows is the operating system of choice for the majority of Local users, and while Local is compatible with Windows, below we will break down some common troubleshooting steps for Windows users to ensure they can enjoy all of Local’s features!
Table of Contents:
Supported Windows Versions
Local supports Windows 10 (64-bit) and Windows 11. As of version 8.3, Local no longer supports 32-bit Windows versions. You can read more about Local’s minimum requirements here.
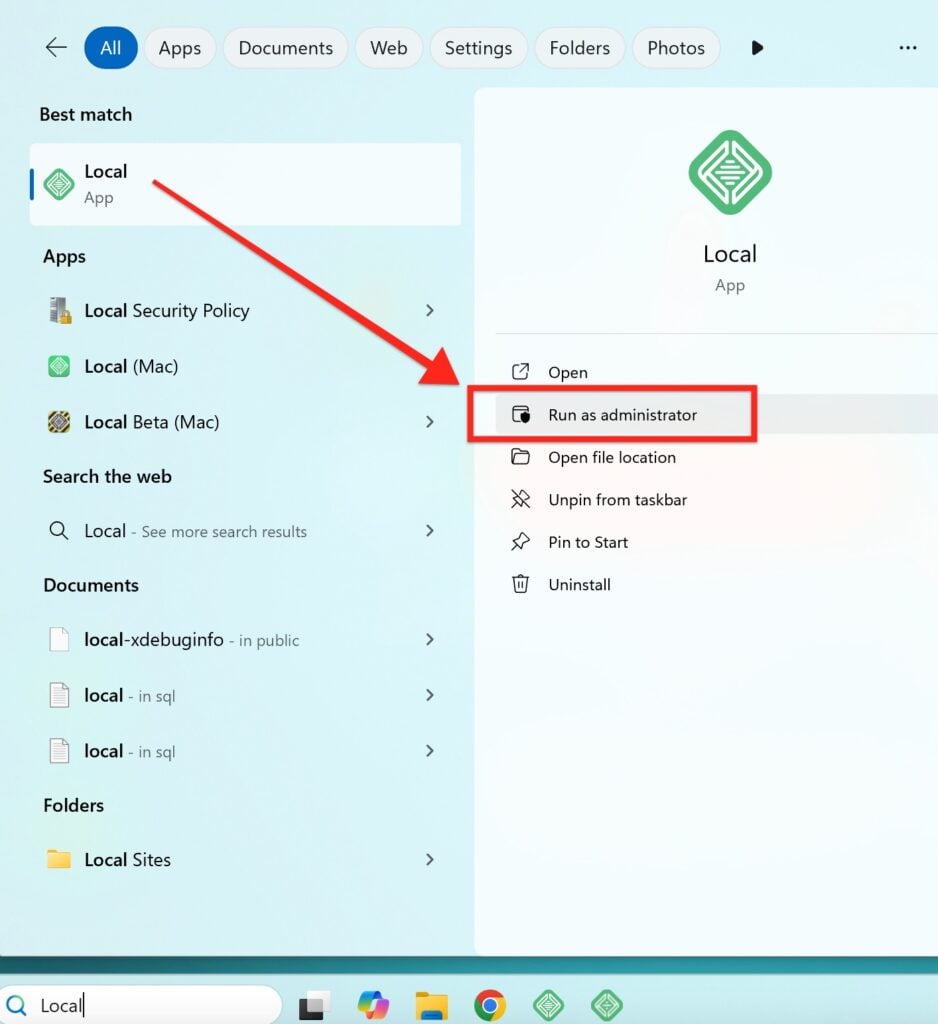
Running Local as Administrator
Running an application like Local as an administrator gives it elevated privileges that can sometimes resolve issues where Local might be blocked by a security or permissions setting. You can search for the app from your desktop and make that selection here:
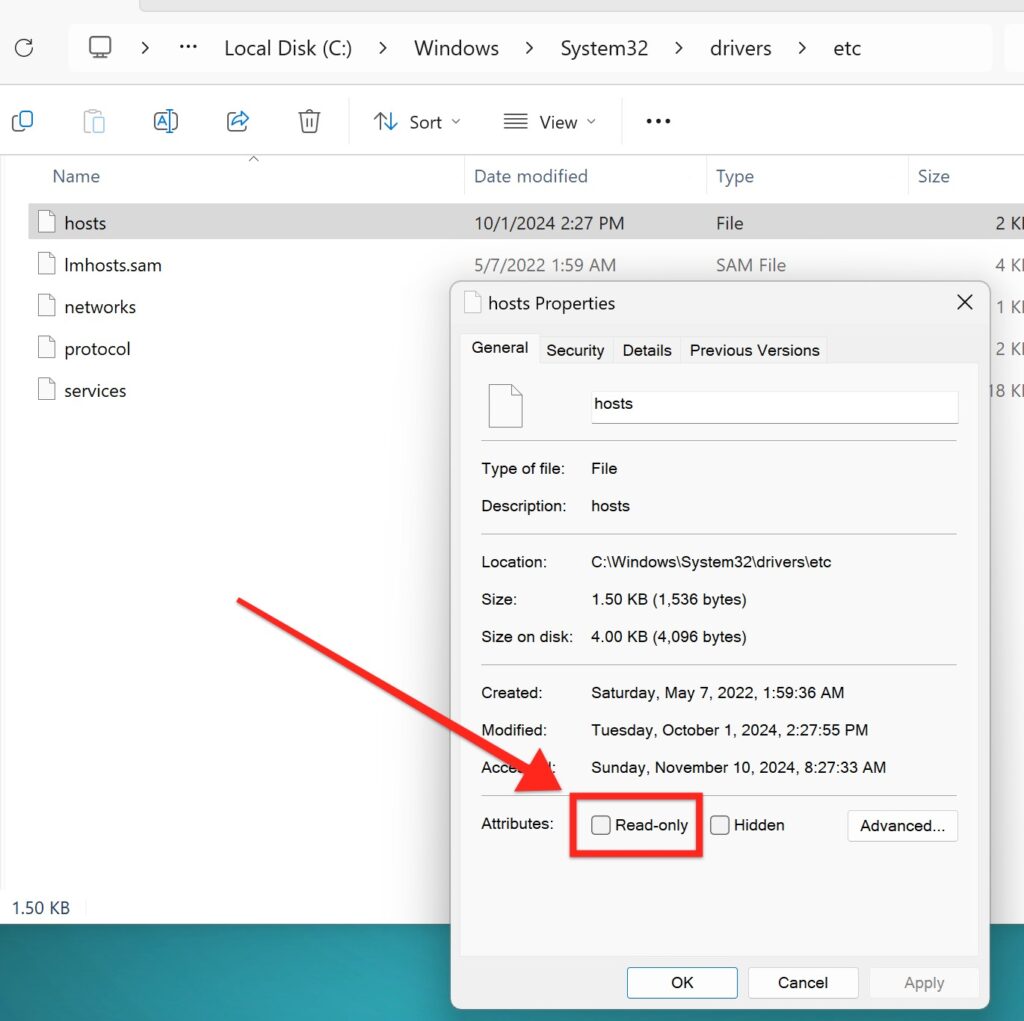
Remove Read-only Attribute
In order for Local to add, edit or remove the domains of sites you create in the app, it needs access to the Hosts file on your machine. Sometimes the permissions for this file are set to Read Only mode. To check and change this setting follow these steps:
- Go to C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
- Right-click on the hosts file and go to “Properties”
- Uncheck “Read-only”
- Click “Apply”
- Re-open Local
Common Security Blockers
Sometimes Local needs to be allowed through the Windows Defender Firewall in order to proceed. From your Windows Security area, you can select Firewall and Network protection, then “Allow an app to communicate through Windows Firewall” and select local.exe.

It’s possible that Windows Defender is not the culprit, but there are still many other antivirus, security, or firewall applications that could be blocking Local. Below are some of the most common with links to their documentation for troubleshooting. This isn’t an exhaustive list, so if you’re unsure, you might have to search your device to see what other security applications might be installed.
note
Employer Security
If your device is issued by your employer or you’re using a network managed by them, some security settings may restrict features in Local. Check the links below for the URLs and ports Local uses, and share this information with your IT department to make the most of Local.
Allow Local to Make Changes
Your device will ask for permission whenever Local needs to make changes to certain things outside of the app. For example, when adding or removing sites or editing domains, Local needs to update the hosts file and SSL certificates on your device. You’ll need to watch for these prompts and let the device know that you are allowing Local to proceed. If you’re not seeing prompts like the ones below, then something may be blocking access (see other sections of this article). If you do get to the second prompt, you’ll want to make sure to select Yes.
note
If you only get the first prompt in the corner, try clicking on the three dots next to the X, and Go to notification settings to ensure those are enabled.
If you still do not see the prompts above at any point when creating new sites, you might be running into the same issue as described here in our Local Community Forums. This user resolved the problem by correcting some broken PATH variables on their machine. Follow the hyperlink above for their helpful guide with screenshots for more information.
Performance Issues
Due to differences in the file system and firewalls, some Windows users have reported issues with the Local app as well as slow site performance. Thankfully, there are some tips and tricks to get around these pesky Windows-specific issues:
- What domain suffix is your site using? Some users have seen significant speed improvements by changing their site domain from .local to another value (.abc for example). The site domain can be set during site creation or edited after the site has been created. A global default for new sites can be set in Local’s Preferences.
- What folder is your site saved in? Some users have seen significant speed improvements by moving their site out of the default path (C:\Users\{user-name}\Local Sites) and placing the site in another folder. This file path can be set during site creation. A global default for new sites can be set in Local’s Preferences.
note
There is a known Windows issue in Local for those utilizing MariaDB. We have a post in the forums here for users to vote, comment or follow along. Switching to MySQL should return performance back to normal, however if this is not an option some have found this article from MariaDB helpful.
If you’re still having trouble with speed in the Local app, you can check out our full performance troubleshooting article here for more helpful tips.
Known Windows Issues
- Special Characters in Windows Username
There is currently a Windows bug where users with special characters in their usernames, including spaces, are unable to create sites. The workaround is simply to create a new user without any special characters or spaces, and then you should be able to proceed. Here are some examples of those errors:

- Special Characters in WordPress Username or Password
Similarly to the above, if you try to create a site and have utilized special characters or spaces in your WordPress credentials you will run into errors like these below. The easiest solution will be to delete that site, and start again but utilizing credentials without those items.